Chroma Subsampling – 4:4:4 Vs 4:2:2 Vs 4:2:0: What is It and Why Does It Matter?

Chroma subsampling is a critical concept when it comes to the digital imaging of color. It refers to the compression of data that occurs when digital images are converted from their original format into a more manageable size.
| Chroma Subsampling | Color Resolution | Common Use Cases |
| 4:4:4 | Full-color resolution | Professional video production, broadcasting, and high-end gaming |
| 4:2:2 | Half color resolution | Broadcast television, satellite transmission, and DVD production |
| 4:2:0 | Quarter color resolution | Streaming video, Blu-ray discs, and digital television |
In this article, we’ll discuss the differences between 4:4:4, 4:2:2, and 4:2:0 chroma subsampling, so you can better understand how they affect image quality.
Chroma subsampling is used in various applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and image processing. All three types of chroma subsampling have their own pros and cons depending on the application they are being used for.
We’ll explore these differences in detail, so you can make an informed decision about which type of chroma subsampling best suits your needs.
How Does Chroma Subsampling Work?
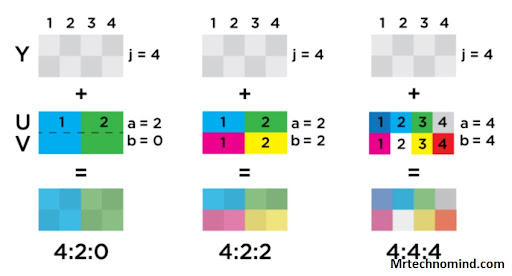
Chroma subsampling is a method used in digital imaging to reduce image file size. It works by reducing the resolution of the color information, rather than the luminance or brightness information, in an image. This allows for a smaller image file size without much loss of visual quality.
The process of chroma subsampling is done on each individual pixel in an image. Color information is represented by three components: Red, Green, and Blue (RGB). Each component has its own bit-depth which represents how many different shades can be displayed for each color.
Chroma subsampling reduces the bit-depth of the color components, most commonly in a 4:2:2 or 4:2:0 ratio. In a 4:4:4 ratio, all three components are equal and no reduction takes place. The 4:2:2 ratio reduces the blue and red component bit-depth by half while the green component remains at full resolution. The 4:2:0 ratio reduces all three components by half compared to the 4:4:4 ratio, resulting in an even smaller image file size but with a more noticeable drop-off in image quality.
With this knowledge, we can explore what chroma subsampling actually is and how it affects our images.
What is Chroma Subsampling?

Chroma subsampling is a method used to reduce the amount of data needed for transmitting images. It works by reducing the resolution of color information while leaving the luminance intact. This technique is often used in HDTVs and digital cameras, as well as video production applications.
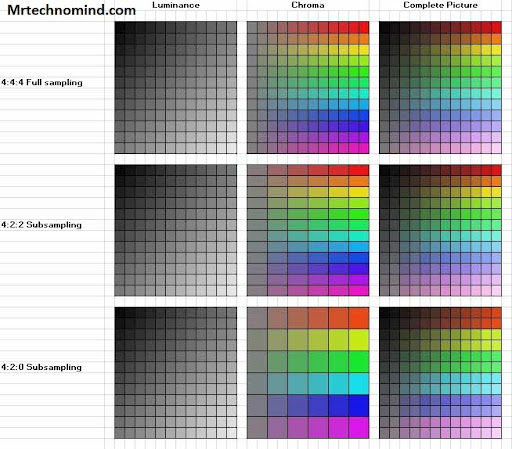
Chroma subsampling has three main variants: 4:4:4, 4:2:2, and 4:2:0. The numbers refer to the ratio of chroma resolution compared to luminance resolution. In 4:4:4 mode, each pixel contains full chroma information; in 4:2:2 mode, two pixels share one set of chroma information; and in 4:2:0 mode, four pixels share one set of chroma information.
In terms of image quality, it’s important to note that all three variants offer different trade-offs between color accuracy and file size. For example, 4:4:4 provides flawless color accuracy but requires more storage space due to its high data rate. On the other hand, 4:2::0 sacrifices some color accuracy but reduces file size significantly.
With this in mind, it’s best to understand which variant is most appropriate for your specific use case – whether that be a high-end home theater display or a mobile device with limited storage space. Depending on your needs you may want to prioritize either color fidelity or overall file size when selecting which variant is right for you.
How to Activate 4:4:4 on Tvs?
Activating 4:4:4 on TVs is easy but requires a bit of knowledge. To illustrate this, consider the experience of my friend who recently bought a new TV. She was so excited to have it in her living room, but when she turned it on and saw the picture, she was disappointed.
After doing some research online, she discovered that her TV didn’t have chroma subsampling set to 4:4:4 by default. Fortunately, she was able to find instructions for how to access the settings menu and adjust the chroma subsampling from 4:2:2 to 4:4:4.
After making the change, my friend noticed an immediate difference in color accuracy and sharpness of her TV’s picture quality. With just one adjustment, her living room felt transformed into a high-definition movie theater! It was amazing how such a small change could make such a big impact on the overall television viewing experience.
Changing your TV’s chroma subsampling setting is an easy way to improve image quality without spending any extra money. While this works great on TVs, it’s not quite as straightforward when you move onto other devices like monitors or projectors; these need different settings depending on their type and resolution capabilities. That’s why we should now take a look at chroma subsampling specifically for monitors and other display devices.
Chroma Subsampling on Monitors

Chroma subsampling is a method of compressing digital video data by reducing the amount of color information that is sent over a transmission line. This technique helps to reduce bandwidth requirements for transmitting video signals. The three main types of chroma subsampling are 4:4:4, 4:2:2, and 4:2:0.
The difference between each type lies in how they represent the color information. 4:4:4 represents all of the available color information without compression and is considered to be the best quality option. It is often used with high-end monitors and televisions to ensure accurate color reproduction. On the other hand, 4:2:2 and 4:2:0 compress the color information by combining pixels together in order to reduce bandwidth requirements, resulting in slightly lower image quality but still providing good results for most applications.
When choosing a monitor or television for your needs, it’s important to consider which type of chroma subsampling you need based on your particular use case. For example, if you’re looking for accurate color reproduction then you should opt for a monitor with 4:4:4 support, while if you’re looking for general viewing purposes then either 4:2:2 or 4:2:0 will provide adequate results at a lower cost.
Understanding what type of chroma subsampling you need can help you make an informed decision when purchasing your next monitor or television set. With this knowledge in hand, we can move on to discuss Display Stream Compression (DSC) technology which provides further reductions in video data transmission size without compromising image quality.
Dsc (Display Stream Compression)
Chroma subsampling is the process of reducing the amount of data used to represent a digital image.
Similarly, Display Stream Compression (DSC) is a technique that reduces the bandwidth required to transmit an image across a display connection.
It is like squeezing a balloon – by compressing it, you can fit more air inside while still having the same shape and size as the balloon.
DSC works by compressing each frame of video as it is sent from source to display.
This allows for higher resolutions such as 4K and 8K to be transmitted over HDMI, USB-C, and other connectors with a much lower bandwidth than otherwise needed.
DSC also supports chroma subsampling which allows for images to be stored in smaller file sizes with no perceivable difference in visual quality.
The advantage of using DSC is that it can reduce data transmission times and allow for higher-resolution content without bogging down your computer or network connection.
This makes it ideal for applications such as streaming media, gaming, or any other situation where image clarity is important but quick response times are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Are the Benefits of Using Chroma Subsampling?
Chroma subsampling is a great way to improve the quality of video and audio recordings.
It reduces the amount of data stored in a file, which can save storage space and bandwidth while maintaining a high-quality audio or video experience.
The benefits include improved color accuracy, reduced artifacts, and increased compression ratio.
In addition, chroma subsampling can help reduce encoding time and minimize banding issues.
2. How Does Chroma Subsampling Affect Image Quality?
Chroma subsampling affects image quality by reducing the amount of color information during compression. This can lead to a loss of detail and color accuracy, especially noticeable in areas of high chroma complexity.
It’s important to consider how the different subsampling ratios (4:4:4 vs 4:2:2 vs 4:2:0) affect the overall quality of the image when making decisions about which one to use.
3. What is the Difference Between 4:4:4 and 4:2:2?
Like a prism splitting light into its component colors, chroma subsampling divides an image’s color information into distinct parts. The difference between 4:4:4 and 4:2:2 lies in how much of that information is kept.
4:4:4 preserves all the color data, while in 4:2:2, one-half of the color information is discarded. This makes 4:2:2 a less accurate representation of the original image but reduces file size and data transmission requirements, making it more suitable for streaming video.
4. Are There Any Drawbacks to Using Chroma Subsampling?
When using chroma subsampling, there are a few drawbacks to consider.
The most notable one is that the image resolution of the color information is decreased due to the fact that it is being compressed into fewer bits.
Additionally, this can result in a loss of color accuracy and detail in areas where the hue changes rapidly.
Furthermore, certain types of compression artifacts can become visible which can be especially noticeable in darker images.
5. Does Chroma Subsampling Have Any Effect on Audio Quality?
Chroma subsampling does have an effect on audio quality. The amount of color information that is removed by chroma subsampling can cause a noticeable degradation in audio quality, especially when listening to certain instruments or vocals.
This is because the amount of color information that is removed affects the accuracy of the sound being reproduced. When using chroma subsampling, it’s important to choose one that best suits the needs of your audio production, as different levels of chroma subsampling can drastically change the final output.
Conclusion
Chroma Subsampling is a powerful tool for reducing the amount of data required to store an image or audio file. It allows us to achieve the better image and sound quality with fewer data, making it a great choice for storing media files.
When used properly, 4:4:4 and 4:2:2 can produce near-lossless results, while 4:2:0 offers good quality at the cost of some detail. Interestingly, studies have shown that the human eye cannot detect any differences between 4:4:4 and 4:2:0 when viewing images on LCD screens.
Overall, Chroma Subsampling is a great way to reduce storage space without sacrificing too much in terms of quality. While there are some drawbacks to using it, such as reduced detail in certain colors, these can generally be avoided by using the right settings.
In addition, Chroma Subsampling has no effect on audio quality whatsoever. With its benefits outweighing its drawbacks, Chroma Subsampling is definitely worth considering when dealing with large media files.