Ips Vs Oled – Which Panel Type Should I Choose?

Are you looking to upgrade your display technology? With so many options on the market, deciding which panel type is right for you can be overwhelming.
Two of the most popular types are IPS and OLED. But what exactly are these technologies, and how do they compare?
IPS (In-Plane Switching) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) offer incredible picture quality but distinct performance, price, and suitability differences for different uses.
In this article, we’ll explore the pros and cons of each panel type to help you decide which is best suited for your needs. Whether you’re a gamer, a graphic designer, or simply someone who wants a top-notch viewing experience, understanding the differences between IPS and OLED will help you choose the perfect display for your setup.
So let’s dive in!
Ips Vs Oled – Which Panel Type Should I Choose?
| Panel Type | IPS (In-Plane Switching) | OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) |
| Image Quality | Good color accuracy and wide viewing angles. | Excellent color reproduction, deep blacks, and high contrast ratio. |
| Brightness | Typically lower brightness compared to OLED. | OLED panels can achieve higher brightness levels. |
| Contrast Ratio | Moderate contrast ratio. | High contrast ratio due to individually lit pixels. |
| Response Time | Generally slower response time, which can result in motion blur. | Very fast response time, ideal for fast-paced content like gaming. |
| Burn-in Risk | Minimal risk of burn-in. | OLED panels have a higher risk of burn-in if static images are displayed for long periods. |
| Price | Generally more affordable compared to OLED. | OLED panels tend to be more expensive. |
| Availability | Commonly found in a wide range of devices and sizes. | OLED panels are predominantly used in high-end smartphones and premium TVs. |
Picture this: you’re in the market for a new TV or phone, and you’re faced with the choice between IPS and OLED displays. Which one should you choose? This is a question that many consumers grapple with, as both types of panels have their strengths and weaknesses.
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching, a type of LCD technology first introduced by Hitachi in 1996. One of the critical advantages of IPS panels is their wide viewing angles – this means that the image quality remains consistent even when viewed off-axis. IPS displays also have better colour accuracy and brightness than other LCD technologies.
On the other hand, OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Unlike LCDs, which require a backlight to illuminate the pixels, each pixel on an OLED display emits its light. This allows for true blacks, infinite contrast ratios, vibrant colours, and fast response times.
So, which one should you choose? It ultimately depends on your priorities and how you plan to use your device. An IPS panel may be the way to go if colour accuracy and viewing angles are necessary. However, if you want deep blacks and vivid colours for movie-watching or gaming, OLED could be the better option.
Next up: let’s take a closer look at some of the pros and cons of each panel type to help you make an informed decision.
Oled Vs. Ips
We’ve already discussed the differences between IPS and OLED panels, but now let’s dive deeper into the debate of OLED vs. IPS. Both have unique strengths and weaknesses, so which should you choose?
OLED screens are known for their deep blacks, vibrant colours, and energy efficiency. They also have a faster refresh rate than IPS panels, making them ideal for gaming or watching action-packed content. However, OLED screens can suffer from image retention/burn-in if static images are too long on the net.
On the other hand, IPS panels have wider viewing angles and are more affordable than OLED screens. They also don’t suffer from image retention/burn-in as OLEDs do. However, they tend to have lower contrast ratios and slower response times.
When deciding between OLED vs. IPS, it ultimately comes down to your personal preference and what you’ll be using your device for. If you prioritize high-quality visuals and don’t mind spending extra money, an OLED screen may be worth it. But if affordability and avoiding image retention/burn-in is essential to you, then an IPS panel is the way to go.
Now, look at OLED image retention/burn-in and how to prevent it.
Oled Image Retention/burn-in
On the other hand, OLED panels are known for their stunning image quality and deep blacks. However, one potential issue with OLED displays is image retention or burn-in. This occurs when a static image is displayed on the screen for an extended period, causing it to become permanently imprinted into the panel.
This can be particularly problematic for those who use their devices for gaming or watching TV shows with static logos. To combat this issue, manufacturers have developed technologies such as pixel shifting and screen savers that prevent static images from remaining on the screen for too long. Additionally, newer OLED panels are less prone to burn-in due to improved manufacturing processes and materials.
Not all users will experience burn-in, and it typically takes thousands of hours of usage before any signs appear. Overall, while OLED panels have drawbacks such as image retention, they offer unparalleled image quality and deep blacks that many users find worth the risk. As technology continues to improve, we can expect even more advancements in OLED display technology that further mitigate these issues.
Moving forward, it’s essential to consider panel type and factors such as screen size when choosing a device. Larger screen size may be preferable for those who enjoy immersive experiences such as gaming or watching movies. In contrast, a smaller screen may be more practical for those who need portability or ease of use. Consider your specific needs and preferences when deciding between IPS vs OLED panels.
Screen Size

When choosing a screen size, there are a few factors to consider. First and foremost, what will you be using your device for? A larger screen may be preferable for watching movies or playing games. However, a smaller screen may be the way to go if portability is essential.
Another factor to consider is resolution. A higher resolution can make images and text appear sharper and more detailed. This can be especially important if you use your device for work or other tasks requiring reading small text or viewing fine details.
It’s also worth considering how the device will fit into your daily life. Will it primarily be used at home, or will you need to take it on the go? If the latter is true, a smaller screen may be more practical.
When it comes down to it, the best screen size for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. Take some time to think about how you’ll be using your device before making a decision. And remember, if you need help determining which size is right for you, many manufacturers offer machines in a range of sizes so that you can find the perfect fit.
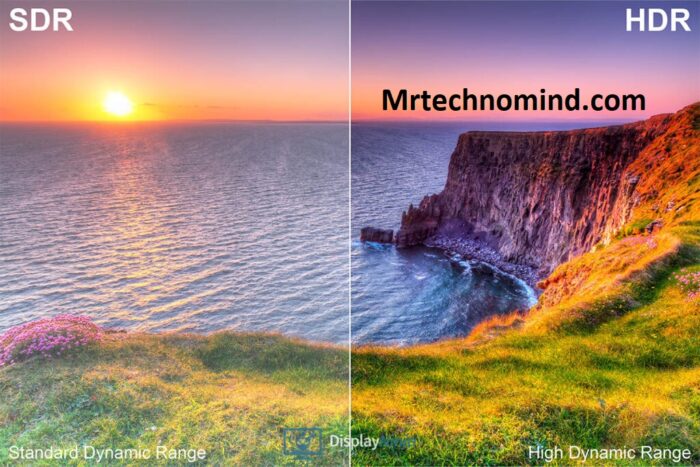
As technology advances, one feature that has become increasingly popular is high dynamic range (HDR). HDR refers to the ability of a display to produce a broader range of colours and brightness levels than traditional displays. This can result in more vivid and lifelike images.
If you value picture quality above all else, HDR may be essential when choosing a display. However, only some content is optimized for HDR displays yet, so depending on what you plan on watching or playing, the benefits of HDR may soon be apparent.
When choosing a display size and type, you must consider your needs and preferences and any advanced features like HDR that could enhance your viewing experience. With so many options available, there’s sure to be a perfect display for everyone.
Hdr (High Dynamic Range)

| HDR Format | HDR10 | Dolby Vision | HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma) |
| Dynamic Range | Static metadata, fixed peak brightness and color grading for the entire content. | Dynamic metadata, allows for scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame adjustments to optimize brightness and color. | Hybrid format, supports both standard dynamic range (SDR) and HDR content. |
| Compatibility | Widely supported across various devices and platforms. | Less common, mainly found in higher-end TVs and streaming services. | Mainly used in broadcasting, particularly for live TV and sports events. |
| Color Depth | 10-bit color depth, providing over 1 billion colors. | Supports both 10-bit and 12-bit color depth, offering over 68 billion colors. | Supports both 8-bit and 10-bit color depth, depending on the content. |
| Peak Brightness | Maximum peak brightness is typically up to 1,000 nits. | Can reach higher peak brightness levels, often up to 4,000 nits or more. | Similar to HDR10, with a typical peak brightness of up to 1,000 nits. |
| Content Availability | Widely available across various streaming services, Blu-ray discs, and gaming consoles. | Limited content compared to HDR10 but growing library across streaming platforms. | Mainly used for live broadcasting, particularly in certain regions and specific applications. |
HDR (High Dynamic Range) is a display technology that has recently become popular. It is an innovation that provides a higher level of contrast and colour accuracy, resulting in a more immersive viewing experience.
HDR-enabled displays can produce brighter whites and darker blacks, which leads to a more dynamic image. One significant advantage of HDR technology is that it enhances the overall picture quality, making everything appear more realistic.
This realism means that you can see details in the pictures that were previously invisible, which gives an entirely new dimension to your viewing experience. The colours are also more vibrant, giving you a more vivid and enjoyable viewing experience.
Another advantage of HDR technology is that it makes it easier to notice subtle changes in lighting conditions. This means you can enjoy your favourite movies or TV shows even if they have scenes with different lighting conditions. You will get all detail because HDR technology lets you see everything.
HDR technology is an excellent option for those wanting the best visual experience. Whether watching movies or playing video games, HDR-enabled displays will provide fantastic picture quality.
The next section’ll discuss how this technology can take gaming to the next level.
Gaming

Gamers demand the best visual experience when playing their favourite games. The panel type of your monitor plays a crucial role in ensuring you get the most out of your gaming experience. IPS and OLED panels have their benefits, but which one should you choose for gaming?
When it comes to colour accuracy, IPS panels are the clear winner. They offer vibrant colours and excellent viewing angles, making them perfect for gamers who enjoy visually stunning games. Additionally, IPS panels have lower input lag than OLED panels, providing a smoother gaming experience.
However, OLED panels excel in contrast ratio and black levels. This makes them ideal for gamers who play in dark environments or want to simultaneously experience deep blacks and vivid colours. OLED panels also offer faster pixel response times than IPS panels, reducing motion blur during fast-paced games.
To help you decide which panel type is right for you, here are four factors to consider when choosing between an IPS and OLED panel:
- Color accuracy
- Viewing angles
- Contrast ratio
- Black levels
Ultimately, whether you choose an IPS or OLED panel depends on your personal preferences as a gamer. Do you prioritize colour accuracy or contrast ratio? Do you play mostly in bright or dark environments? Answering these questions can guide your decision-making process.
As we move forward into our discussion on response time, it’s important to note that this factor is closely tied to the overall performance of both IPS and OLED panels in gaming scenarios.
Let’s take a closer look at how response time affects your gameplay experience on each panel type.
Response Time
| Panel Type | Response Time |
| OLED | Very fast response time, typically around 0.1 milliseconds (ms) or less. |
| IPS (In-Plane Switching) | Moderate response time, usually around 4-8 ms. |
| TN (Twisted Nematic) | Fast response time, typically around 1-2 ms. |
| VA (Vertical Alignment) | Moderate to slow response time, ranging from 4-8 ms or more. |
Rapid response time remains the rave in the world of technology today. Response time is the duration for a pixel to change from one colour to another. It’s measured in milliseconds (ms).
The better the response time, the less blur you’ll see when viewing fast-paced video content or playing games that require quick reflexes. A high response time leads to motion blur, resulting in ghosting on your display.
If you’re an avid gamer or a movie enthusiast, choosing a panel type with a low response time is critical. Without this feature, images will appear blurry and distorted. Most OLED panels have a response time of fewer than 0.1 ms, significantly faster than most IPS panels that average around 5 ms.
OLED screens are more responsive and have less motion blur than IPS displays. So, if rapid response time is vital, an OLED panel might be your best option. As you consider your panel choice, remember that not all OLEDs are created equal, just as not all IPS panels operate at the same speed.
So ensure you check product reviews and specifications before making your final choice. Remember that even though OLEDs offer exceptional picture quality and speedy performance, they cost more than their IPS counterparts.
Refresh Rate & Resolution
| Panel Type | Refresh Rate | Resolution |
| OLED | Variable, commonly available with high refresh rates such as 60Hz, 90Hz, 120Hz, or even 240Hz. | Varies depending on the device, ranging from HD (720p) to 4K Ultra HD (2160p). |
| IPS (In-Plane Switching) | Variable, commonly available with refresh rates ranging from 60Hz to 240Hz. | Varies depending on the device, ranging from HD (720p) to 4K Ultra HD (2160p). |
| TN (Twisted Nematic) | Variable, commonly available with high refresh rates such as 144Hz, 240Hz, or even higher for gaming monitors. | Varies depending on the device, ranging from HD (720p) to 4K Ultra HD (2160p). |
| VA (Vertical Alignment) | Variable, commonly available with refresh rates ranging from 60Hz to 144Hz. | Varies depending on the device, ranging from HD (720p) to 4K Ultra HD (2160p). |
There are several factors to consider when choosing between IPS and OLED panels. One of the most important factors is the refresh rate and resolution of the display.
The refresh rate refers to how often the screen is redrawn per second, while the resolution is the number of pixels on the net. A higher refresh rate means smoother motion and less blur in fast-moving scenes, which is especially important for gamers or those who watch many action movies. Regarding resolution, a higher number of pixels means sharper images and more detail on the screen.
However, some may only need a higher refresh rate and resolution. A lower refresh rate and resolution may suffice for everyday use, such as browsing the web or watching videos.
To help you make an informed decision, here are some key things to consider when looking at refresh rate and resolution:
– What kind of content will you be using your display for? Gaming and fast-paced action require higher refresh rates.
– Do you need high-resolution for photo or video editing?
– Are you willing to pay more for a display with higher specs?
– Do you have graphics cards or devices that can support high-end displays?
Ultimately, when it comes down to choosing between IPS vs OLED panels, every user’s needs are different. Consider your budget, usage habits, and personal preferences before deciding.
As technology evolves rapidly, the one-panel type has been gaining attention lately: QD-OLED. This innovative new technology combines quantum dot displays with OLED technology to create even more vibrant colours and deeper blacks than traditional OLED displays.
In the next section, we’ll look at this exciting new development in display technology.
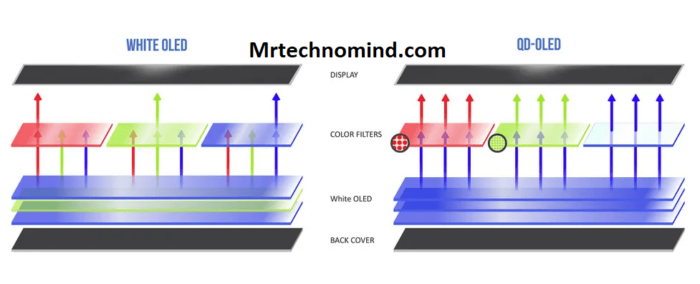
Qd-oled
| Panel Type | Longevity | Power Consumption | Design |
| OLED | The organic materials in OLED panels can degrade over time, leading to potential image retention and reduced lifespan. However, with proper usage and technology advancements, OLED panels can still have a reasonably long lifespan. | OLED panels are known for their power efficiency. Each pixel is individually lit, allowing for precise control and energy-saving benefits, especially when displaying darker content with black areas. | OLED panels offer flexibility in design due to their thin and lightweight structure. They can be used to create curved displays and provide a wide viewing angle experience. |
| IPS (In-Plane Switching) | IPS panels generally have a longer lifespan compared to OLED panels. | IPS panels tend to consume more power due to the need for a backlight to illuminate the pixels uniformly. However, advancements in LED backlighting have improved energy efficiency. | IPS panels are commonly used in a variety of devices and offer a traditional flat screen design. They provide wide viewing angles and good color accuracy. |
| TN (Twisted Nematic) | TN panels typically have a long lifespan. | TN panels have relatively low power consumption compared to other panel types. | TN panels are commonly used in gaming monitors due to their fast response times, but they generally have limited viewing angles and color accuracy. They often have a standard flat screen design. |
| VA (Vertical Alignment) | VA panels generally have a long lifespan. | VA panels consume moderate to high power depending on the specific model and backlighting technology. | VA panels offer good contrast ratios and deep blacks but may have narrower viewing angles than IPS panels. They are commonly used in TVs and some computer monitors. |
While IPS and OLED panels have distinct characteristics, another type of display technology has been making waves in the industry – Quantum Dot OLED or QD-OLED. This new panel type combines the benefits of both IPS and OLED while addressing some of their limitations.
QD-OLED uses a layer of quantum dots to enhance colour accuracy and brightness, similar to how they are used in QLED displays. This allows for more vibrant and lifelike colours compared to traditional OLED panels. At the same time, it also offers the deep blacks and infinite contrast ratio that OLED is known for.
Regarding response time, QD-OLED is faster than IPS but slower than regular OLED panels. However, it still performs well enough for most users and can even provide better motion handling when combined with other technologies like Black Frame Insertion (BFI).
To give you a clearer picture of how QD-OLED compares to IPS and OLED, here’s a table summarizing their key features:
| Feature | IPS | OLED | QD-OLED |
| Contrast Ratio | Good (1000:1) | Excellent (Infinite) | Excellent (Infinite) |
| Color Accuracy | Good (sRGB ~100%) | Excellent (>90% DCI-P3) | Excellent (>90% DCI-P3) |
| Response Time | Fast (~4ms) | Fastest (<1ms) | Faster than IPS but slower than regular OLED |
| Peak Brightness | Good (300-400 nits) | Excellent (700-800 nits) | Excellent (700-800 nits or higher) |
As you can see, QD-OLED offers a compelling combination of features, making it an attractive option for those who want the best of both worlds. It delivers superior colour accuracy and contrasts while providing good response times and peak brightness. However, other factors are still to consider when choosing a panel type, such as longevity, power consumption, and design.
We will explore these other important considerations and how they impact your decision-making process. By understanding all the different aspects of choosing a display panel, you can make an informed decision that suits your needs and preferences.
Longevity, Power Consumption and Design
Some believe OLED displays have a shorter lifespan than their IPS counterparts, but this is not necessarily true. While early models of OLED displays did have issues with burn-in and degradation over time, modern OLED technology has improved significantly. Many manufacturers now offer warranties for their OLED displays comparable to those for IPS panels.
Regarding power consumption, OLED displays typically use less power than IPS panels. This is because each pixel in an OLED display emits its light, whereas an IPS panel relies on a backlight to illuminate the entire screen. As a result, when displaying predominantly black content (such as in dark mode), an OLED display can consume very little power.
Design-wise, both panel types have their strengths and weaknesses. IPS panels generally offer better viewing angles and colour accuracy than OLED displays. However, OLED displays can achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios than IPS panels. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on your specific needs and preferences.
In terms of price, there is no clear winner between IPS and OLED displays. While initially more expensive than equivalent-sized IPS panels, the cost of OLED displays has steadily decreased over the past few years. Some high-end IPS panels can be just as expensive (if not more so) than entry-level OLED displays. Therefore, it is essential to consider all factors – including longevity, power consumption, design, and price – when deciding which panel type to choose.
Price
When choosing between IPS and OLED panel types, price is a significant factor that needs to be considered. OLED panels are known for their high-end features and superior picture quality but come with a hefty price tag. On the other hand, IPS panels are more affordable and offer decent visuals.
An IPS panel might be the way to go if you’re on a tight budget. They’re widely available at different prices and offer great value for money.
However, if you’re looking for the best picture quality, OLED panels are worth the investment. They provide deep blacks and vibrant colours that any other display technology can’t match.
It’s important to note that while OLED panels may seem expensive upfront, they can save you money in the long run due to their energy efficiency. They consume less power than traditional LCDs, which means lower electricity bills over time.
So, if you’re willing to spend more upfront, an OLED panel could be a cost-effective choice in the long term.
In summary, price is important when deciding between IPS and OLED panel types. While IPS panels are more affordable and offer good value for money, OLED panels provide superior picture quality and energy efficiency over time. Ultimately, it depends on your budget and priorities – whether you want to save money upfront or invest in premium display technology for an optimal viewing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Ips Panels Display True Blacks Like Oled Panels?
Have you ever wondered if IPS panels can display true blacks like OLED panels?
Well, the answer is not quite. While IPS displays have come a long way regarding colour accuracy and contrast, they still cannot match the deep blacks that OLED panels can produce.
However, IPS panels should be considered. They excel in viewing angles and brightness, making them an excellent option for those who prioritize these features in their display.
Ultimately, the decision between IPS and OLED comes from personal preference and intended use.
2. How Does the Response Time of Oled Compare to Ips?
Regarding response time, OLED panels are known for being lightning-fast. They can quickly switch from one colour to another, producing smooth and seamless visuals for games or movies.
On the other hand, IPS panels have a slower response time, which may result in motion blur or ghosting. However, this doesn’t mean IPS panels are inferior – they still have advantages, such as wider viewing angles and better colour accuracy.
Ultimately, the choice between OLED and IPS depends on what you prioritize most in your display technology.
3. Are Oled Panels More Prone to Screen Burn-in Than Ips Panels?
Screen burn-in is a common concern among those considering OLED panels. While IPS panels are generally not prone to this issue, OLEDs have been known to experience screen burn-in over time. However, it’s important to note that this is a more minor problem than it used to be, thanks to technological advancements.
Manufacturers have implemented measures such as pixel shifting and automatic brightness adjustments to prolong the lifespan of OLED screens. Plus, the benefits of an OLED panel – such as deeper blacks and more vibrant colours – may outweigh the risk for some users.
Ultimately, it’s up to the individual to weigh the pros and cons and decide which panel type is best for their needs.
4. Does Screen Size Affect the Choice Between Ips and Oled?
Choosing the right panel type for your device ensures an optimal viewing experience. But does screen size matter when choosing between IPS and OLED panels?
The answer is a resounding yes! In fact, the larger the screen size, the more critical it becomes to choose an OLED panel. Why, you ask? OLED boards have better contrast ratios and deeper blacks, creating a more immersive and enjoyable viewing experience.
So if you’re looking for innovation and want to take your viewing experience to the next level, opt for an OLED panel on your larger devices. It’s worth it!
5. Which Panel Type is Better for Graphic Design Work?
For graphic design work, the panel type you choose can make a significant difference in the quality of your final product.
While IPS and OLED panels have advantages, some key differences exist.
OLED panels offer better contrast ratios and deeper blacks, which can be crucial for accurately representing colours and details in your designs.
On the other hand, IPS panels typically offer better colour accuracy and wider viewing angles, which can be helpful when collaborating with others or working on larger projects.
Ultimately, the choice between IPS and OLED will depend on your specific needs as a graphic designer and the types of projects you typically work on.
Conclusion
When choosing between IPS and OLED panels, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. It ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences.
OLED might be better if you value true blacks over response time. However, if screen burn-in is a concern or you need a larger screen size, IPS may be the way to go.
As for graphic design work, both panel types have their advantages and disadvantages. IPS panels are known for accurate colour reproduction, while OLED boards have a wider colour gamut.
Ultimately, it’s essential to research and consider your needs before deciding. Whether you choose IPS or OLED, both panel types offer high-quality visual experiences that can enhance your overall viewing enjoyment.