The One Thing You Need to Know About Usb Speed

The One Thing You Need to Know About Usb Speed
Are you tired of waiting forever for your files to transfer? Well, there’s one crucial thing you need to know about USB speed that can make a difference in your digital life. USB, or Universal Serial Bus, is a popular connectivity standard for connecting devices like printers, cameras, and external storage drives to your computer. But not all USBs are created equal when it comes to speed.
Regarding USB speed, there are different versions available in the market. The most common ones are USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. USB 2.0, the older version, offers a maximum transfer rate of 480 megabits per second (Mbps). On the other hand, USB 3.0, the newer and faster performance, can achieve transfer rates of up to 5 gigabits per second (Gbps) – a whopping ten times faster than USB 2.0!
So, if you frequently transfer large files or work with high-resolution media, upgrading to USB 3.0 can significantly save you time and frustration. This article will delve deeper into the differences between USB 2.0 and 3.0 and why USB speed matters daily.
What is Usb?

So, you’re probably wondering, ‘What’s the deal with USB?’ Well, let me break it down for you: USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, and it’s a fancy way of saying it’s a connection that allows you to plug in all sorts of devices to your computer or laptop.
| Term | Definition |
| Acronym | USB |
| Full Form | Universal Serial Bus |
| Purpose | Standard for connecting devices to computers |
| Introduced | 1996 |
| Types | USB 1.0, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, USB4, USB-C |
| Connector Types | Type-A, Type-B, Mini-USB, Micro-USB, USB-C |
| Speeds | USB 1.0: 1.5 Mbps, USB 2.0: 480 Mbps, USB 3.0: 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.1 Gen 1: 5 Gbps, USB 3.1 Gen 2: 10 Gbps, USB 3.2: 20 Gbps | |
| USB4: 20 Gbps, USB 4.0 Gen 2×2: 40 Gbps | |
| Features | Hot-plugging, Plug-and-play, Power delivery, Data transfer |
| Common Usage | Connecting peripherals (e.g., keyboards, mice, printers) |
| Charging devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets) | |
| Data transfer between devices (e.g., external storage) |
USB covers you whether you need to connect a printer, a keyboard, a mouse, or a smartphone. Its simplicity and versatility have become the standard interface for connecting peripherals to computers.
Now, let’s dive into the different USB versions and what they mean for speed and performance.
USB has undergone several versions as technology advances, each offering faster data transfer speeds. The most common versions you’ll encounter are USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 3.1.
USB 2.0, the oldest and slowest version, has a maximum data transfer rate of 480 megabits per second (Mbps). That may sound pretty fast, but it’s relatively slow compared to the newer versions.
USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, improved significantly with a maximum data transfer rate of 5 gigabits per second (Gbps). This means files can be transferred much quicker, making tasks like backing up data or transferring large media files a breeze.
You may think, ‘Well, USB 3.0 sounds great, but what about USB 3.1?’ USB 3.1, or SuperSpeed+ USB, takes things up a notch with a maximum data transfer rate of 10 Gbps. This increase in speed is particularly beneficial for tasks that involve heavy data usage, such as editing high-resolution videos or working with large databases.
So, if you’re looking for the fastest USB connection available, USB 3.1 is the way to go.
Now that you understand what USB is and the different versions available let’s explore how these speeds can impact your overall experience with USB devices.
Different Usb Versions

To truly grasp the rapid evolution of USB technology, imagine yourself being whisked away on a high-speed journey through the various versions, each unlocking new levels of data transfer efficiency. The first version, USB 1.0, introduced in 1996, offered a maximum transfer rate of 1.5 Mbps. It quickly became apparent that this speed was insufficient for the growing demand for faster data transfer. USB 1.1 was then released, doubling the transfer rate to 12 Mbps, but it still fell short of what users needed.
| USB Version | Speed | Data Transfer Rate | Introduced | Connector Types | Power Delivery |
| USB 1.0 | Low-Speed: 1.5 Mbps | Full-Speed: 12 Mbps | 1996 | Type-A, Type-B | No |
| USB 2.0 | High-Speed: 480 Mbps | 2000 | Type-A, Type-B | No | |
| USB 3.0 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | 2008 | Type-A, Type-B | No | |
| USB 3.1 | SuperSpeed+: 10 Gbps | Gen 1: 5 Gbps | 2013 | Type-A, Type-C | Yes |
| USB 3.2 | SuperSpeed+: 20 Gbps | Gen 2: 10 Gbps | 2017 | Type-A, Type-C | Yes |
| USB4 | 20 Gbps | Gen 2×2: 20 Gbps | 2020 | USB-C | Yes |
Then came USB 2.0, the game-changer. A remarkable transfer rate of 480 Mbps revolutionized how we transferred data. This version brought about the ability to connect high-speed devices like printers, scanners, and external hard drives, making data transfer faster and more efficient. USB 2.0 became the standard for years until the need for even faster transfer speeds arose.
In response to this demand, USB 3.0 burst onto the scene. With a whopping transfer rate of 5 Gbps, it was ten times faster than its predecessor. USB 3.0 introduced a new technology called SuperSpeed, allowing for the rapid transfer of large files and high-definition videos. This version also increased power efficiency, significantly improving speed and energy consumption. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the exciting world of USB speed and discover the one thing you need to know about USB speed.
The evolution of USB versions has brought about significant improvements in data transfer speed, with USB 3.0 being the current standard. However, it is essential to note that the transfer speed of a USB device is not solely determined by the USB version it supports. Other factors, such as the USB cable quality and the connected devices’ capabilities, can also affect the overall speed. In the next section, we will explore the one thing you need to know about USB speed to ensure you make the most of this technology. So, let’s dive deeper into the world of USB speed and uncover the secrets to maximizing your data transfer efficiency.
Usb Speed
USB speed has evolved significantly over the years, unlocking new levels of data transfer efficiency and revolutionizing how we transfer data—with the introduction of USB 2.0, data transfer speeds increased to 480 Mbps, a vast improvement compared to the previous USB 1.1 standard.
| USB Version | Speed | Data Transfer Rate |
| USB 1.0 | Low-Speed: 1.5 Mbps | |
| Full-Speed: 12 Mbps | ||
| USB 2.0 | High-Speed: 480 Mbps | |
| USB 3.0 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | |
| USB 3.1 | SuperSpeed+: 10 Gbps | Gen 1: 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 | SuperSpeed+: 10 Gbps | Gen 2: 10 Gbps |
| SuperSpeed+: 20 Gbps | Gen 2×2: 20 Gbps | |
| USB4 | 20 Gbps | |
| 40 Gbps | Gen 2×2: 40 Gbps |
This allowed for faster and more efficient transfer of files, making it easier to move large amounts of data between devices. However, as technology continued to advance, so did the need for even faster transfer speeds.
USB 3.0 was introduced to meet this demand; offering transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps. This was a significant leap forward in terms of data transfer efficiency. USB 3.0 can transfer a full-length HD movie in seconds, making it ideal for professionals who need to move large files quickly.
USB 3.0 transfers files faster than ever, saving you time and improving productivity.
USB speed 3.0 has become the standard for many devices, offering faster transfer speeds and improved performance. It’s backwards compatible with USB 2.0 and 1.1, so you can still use your older appliances with the newer USB 3.0 ports.
Whether transferring files, backing up data, or connecting peripherals, USB 3.0 provides the necessary speed and efficiency. So, if you’re looking for a faster, more efficient way to transfer data, USB 3.0 is the way to go.
Usb Speed 3.0

Imagine being able to transfer a full-length HD movie in just seconds, revolutionizing the way you move large files and improving your overall productivity. USB 3.0 is here to make that a reality for you.
| USB 3.0 (USB 3.1 Gen 1) | Speed | Data Transfer Rate | Introduced | Connector Types | Power Delivery |
| USB 3.0 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | 2008 | Type-A, Type-B | No | |
| USB 3.1 Gen 1 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | 2013 | Type-A, Type-C | Yes |
With its incredible speed and performance, it’s no wonder why USB 3.0 has become the go-to choice for many tech enthusiasts and professionals. Here are four reasons why USB 3.0 is a game-changer:
- Lightning-fast data transfer: USB 3.0 offers transfer speeds up to 5 gigabits per second (Gbps), which is ten times faster than its predecessor, USB 2.0. Say goodbye to long waiting times when transferring files. With USB 3.0, you can move large amounts of data in a fraction of the time it used to take.
- Enhanced power efficiency: USB 3.0 provides improved power management, allowing devices to consume less power during data transfer. This means you can use your USB-powered devices for longer without worrying about quickly draining their batteries. USB 3.0 also supports increased power output, making it compatible with more power-hungry devices.
- Backward compatibility: USB 3.0 offers significant advancements but doesn’t leave older devices behind. USB 3.0 ports are designed to be backwards compatible with USB 2.0 devices. So, even if you have older gadgets, you can still enjoy the benefits of USB 3.0 by connecting them to a USB 3.0 port.
- Improved connectivity options: USB 3.0 introduces new connector types, such as the USB Type-C, which offers reversible plug orientation and faster data transfer speeds. This means you can connect your devices more easily and enjoy the benefits of USB 3.0 without worrying about which way to plug in your cable.
With all these advantages, USB 3.0 has surpassed its predecessor in speed and performance. But how does USB 3.0 compare to USB 2.0? Let’s dive into the differences and see why USB 3.0 is superior for anyone seeking faster and more efficient data transfer.
Usb 2.0 Vs 3.0
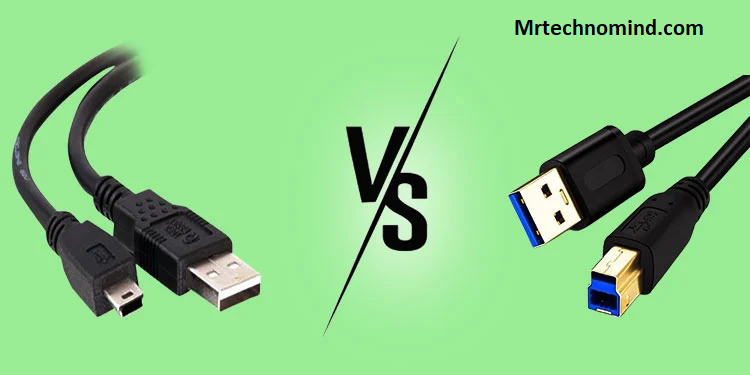
When comparing USB 2.0 and 3.0, there are three key points to consider.
| USB Version | Speed | Data Transfer Rate | Introduced | Connector Types | Power Delivery |
| USB 2.0 | High-Speed: 480 Mbps | 2000 | Type-A, Type-B | No | |
| USB 3.0 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | 2008 | Type-A, Type-B | No | |
| USB 3.1 Gen 1 | SuperSpeed: 5 Gbps | 2013 | Type-A, Type-C | Yes |
First, the two have physical differences, with USB 3.0 having additional pins and a different connector shape.
Second, USB 3.0 provides higher power output, making it ideal for charging devices quickly.
Lastly, compatibility is a factor to consider, as USB 3.0 is backwards compatible with USB 2.0, but you may need an adapter to connect a USB 2.0 device to a USB 3.0 port.
Physical Differences
While exploring the physical differences, it’s crucial to grasp the intricate web of connections that shape USB speed.
USB 2.0 and 3.0 have distinct physical characteristics that impact their data transfer capabilities. USB 2.0 ports usually feature a black or white colour, while USB 3.0 ports are often blue. The most noticeable difference is the physical design of the connectors. USB 2.0 uses a rectangular Type-A connector, whereas USB 3.0 introduces a new Type-A connector with additional pins. This extra set of pins allows for increased data transfer rates and improved performance.
Moreover, USB 3.0 cables contain nine internal wires, while USB 2.0 cables only have four. These additional wires enable USB 3.0 to support faster data transfer speeds.
The physical differences in connectors and cables play a significant role in determining the speed of USB devices. Understanding these distinctions is essential in unlocking the full potential of your USB technology.
Now, let’s move on to the next section and delve into the fascinating world of USB power output.
Power Output
Understanding its power output’s intricacies is crucial to utilize your USB technology’s capabilities fully. The power output of a USB port determines how much power it can provide to connected devices. This is important because different devices have different power requirements.
Here are four key points to know about USB power output:
- USB 1.0 and 2.0 ports typically provide a maximum power output of 500 milliamps (mA). This is sufficient for charging small devices like smartphones and powering low-power peripherals.
- USB 3.0 ports, or USB 3.1 Gen 1, can provide up to 900 mA of power. This allows for faster charging of devices and the use of more power-hungry peripherals like external hard drives.
- USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports can deliver up to 1.5 amps (1500 mA) of power. This increased power output helps charge larger devices like tablets and high-power peripherals.
- USB Power Delivery (USB PD) is a newer standard allowing even higher power output. USB PD can deliver up to 100 watts of power, making it suitable for charging laptops and other high-power devices.
Understanding the power output of your USB ports is essential to ensure you have enough power to charge your devices and connect peripherals. With this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about compatibility and choose the right cables and adapters to maximize the functionality of your USB technology.
Compatibility
If you’re using a USB 2.0 cable, check its compatibility with USB 3.0 ports to ensure optimal data transfer speeds.
Did you know that USB 3.0 ports are backwards compatible with USB 2.0 cables and devices? This means that even though you may not have a USB 3.0 cable, you can still connect your USB 2.0 devices to a USB 3.0 port and they will work fine. However, it’s important to note that when using a USB 2.0 cable with a USB 3.0 port, you will only achieve USB 2.0 speeds. So if you want to take advantage of the faster USB 3.0 speeds, it’s recommended to use a USB 3.0 cable.
Regarding compatibility, it’s also essential to consider the type of USB port you have on your device. USB 3.0 ports are usually coloured blue, while USB 2.0 ports are typically black or white. So before connecting your USB cable, check the colour of the port to ensure that you’re using the correct one.
Using a USB 2.0 cable with a USB 3.0 port will still work, but you won’t be able to take advantage of the faster speeds that USB 3.0 offers. So if you have a USB 3.0 port available, it’s worth investing in a USB 3.0 cable to utilize its capabilities and achieve faster data transfer speeds fully.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I Use a Usb 3.0 Device With a Usb 2.0 Port?
Yes, you can use a USB 3.0 device with a USB 2.0 port. However, the transfer speed will be limited to the maximum speed supported by the USB 2.0 port.
2. How Does Usb Speed Affect File Transfer Time?
USB speed directly affects file transfer time. The faster the USB speed, the quicker files can be transferred. USB 3.0 offers faster speeds than USB 2.0, so using a USB 3.0 device will result in faster file transfers.
3. Are There Any Compatibility Issues When Using Usb 3.0 Devices With Older Computers?
There can be compatibility issues when using USB 3.0 devices with older computers. These computers may not have USB 3.0 ports, so you may need an adapter or a USB 2.0 port instead.
4. Can I Connect a Usb 2.0 Device to a Usb 3.0 Port?
You can connect a USB 2.0 device to a USB 3.0 port. It will work but at USB 2.0 speed. Fun fact: USB 3.0 is 10 times faster than USB 2.0.
5. Are All Usb 3.0 Ports the Same Speed?
Not all USB 3.0 ports are the same speed. The speed can vary depending on the hardware and specifications of the device. It’s essential to check the speed of the port before connecting any devices.
Conclusion
So now you know the one thing you need to know about USB speed. It’s all about the version, baby! USB 3.0 is the way to go if you want lightning-fast data transfer. With its SuperSpeed capability, you can transfer files in a blink of an eye.
Say goodbye to waiting hours for your files to transfer, and say hello to efficiency and productivity. But don’t fret if you’re still stuck with USB 2.0. It may not be as fast as its younger sibling, but it still gets the job done. Remember, slow and steady wins the race. Just be patient, and your files will eventually reach their destination.
As the saying goes, “Rome wasn’t built in a day.”Similarly, USB technology has come a long way from its humble beginnings. It has evolved and improved, giving us faster and more efficient ways to transfer data.
So, whether you’re using USB 2.0 or USB 3.0, remember that the most important thing is to keep moving forward. Embrace the progress and adapt to the changing technology landscape. After all, it’s not about how fast you go, but about the journey itself.